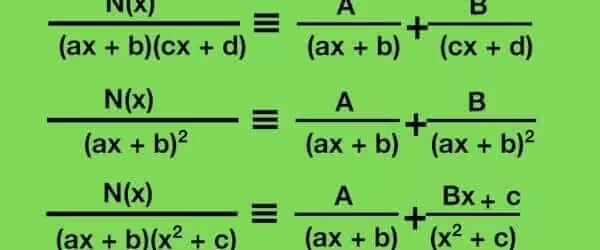Eigenvalue Calculator
Find eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a square matrix with step-by-step solution.
Characteristic Polynomial
Eigenvalues
Eigenvectors
Verification
Use this free eigenvalue and eigenvector calculator to find eigenvalues, eigenvectors, and the characteristic polynomial of any square matrix. Get step-by-step solutions with detailed explanations. Essential for linear algebra and differential equations.
What are Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors?
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors reveal fundamental properties of linear transformations. When a matrix \( A \) acts on an eigenvector \( \mathbf{v} \), the result is simply a scaled version of \( \mathbf{v} \). The scaling factor is the eigenvalue \( \lambda \).
$$ A\mathbf{v} = \lambda\mathbf{v}$$
This equation says that the eigenvector \( \mathbf{v} \) only changes in magnitude (not direction) when transformed by \( A \).
The Characteristic Polynomial
To find eigenvalues, solve the characteristic equation:
$$\det(A – \lambda I) = 0$$
This determinant produces a polynomial in \( \lambda \). The roots of this polynomial are the eigenvalues.
For a 2×2 matrix, the characteristic polynomial is quadratic. For a 3×3 matrix, it’s cubic.
Finding Eigenvectors
Once you have an eigenvalue \( \lambda \), find the eigenvector by solving:
$$(A – \lambda I)\mathbf{v} = \mathbf{0}$$
This is a homogeneous system. The solution space (null space of \( A – \lambda I \)) gives the eigenvectors corresponding to \( \lambda \).
Properties
Trace and Determinant
- Sum of eigenvalues = \( \text{trace}(A) \) (sum of diagonal elements)
- Product of eigenvalues = \( \det(A) \)
Algebraic vs Geometric Multiplicity
- Algebraic multiplicity: how many times \( \lambda \) appears as a root
- Geometric multiplicity: dimension of the eigenspace
Real vs Complex Eigenvalues
Real matrices can have complex eigenvalues, which always come in conjugate pairs.
Applications
Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
Eigenvectors of the covariance matrix identify directions of maximum variance in data.
Stability Analysis
Eigenvalues determine whether a system is stable:
- All \( |\lambda| < 1 \): stable (discrete systems)
- All \( \text{Re}(\lambda) < 0 \): stable (continuous systems)
Quantum Mechanics
Observable quantities correspond to eigenvalues of Hermitian operators.
Google’s PageRank
The importance of webpages is determined by the dominant eigenvector of the link matrix.
Vibration Analysis
Natural frequencies of mechanical systems are eigenvalues of the system matrix.
Special Cases
| Matrix Type | Eigenvalue Property |
|---|---|
| Symmetric | All real eigenvalues |
| Orthogonal | \( |
| Positive definite | All \( \lambda > 0 \) |
| Nilpotent | All \( \lambda = 0 \) |
| Idempotent | \( \lambda = 0 \) or \( 1 \) |
Diagonalization
A matrix \( A \) is diagonalizable if it has \( n \) linearly independent eigenvectors. Then:
$$A = PDP^{-1}$$
Where \( D \) is diagonal (eigenvalues on diagonal) and \( P \) contains eigenvectors as columns.