Definite Integral Solver
Solve the definite integral and visualize the area under the curve.
Result
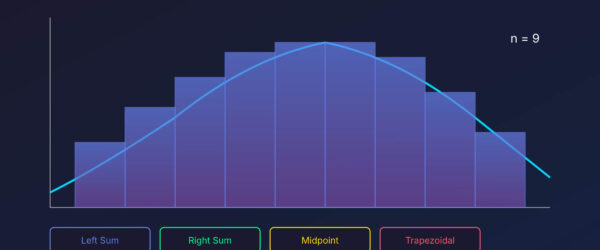
Area Visualization
Calculation Details
Use this free definite integral solver & calculator to compute exact and numerical values of integrals. Enter your function and bounds to get the result with step-by-step antiderivative computation. Perfect for calculus students and anyone needing to calculate areas under curves.
What is a Definite Integral?
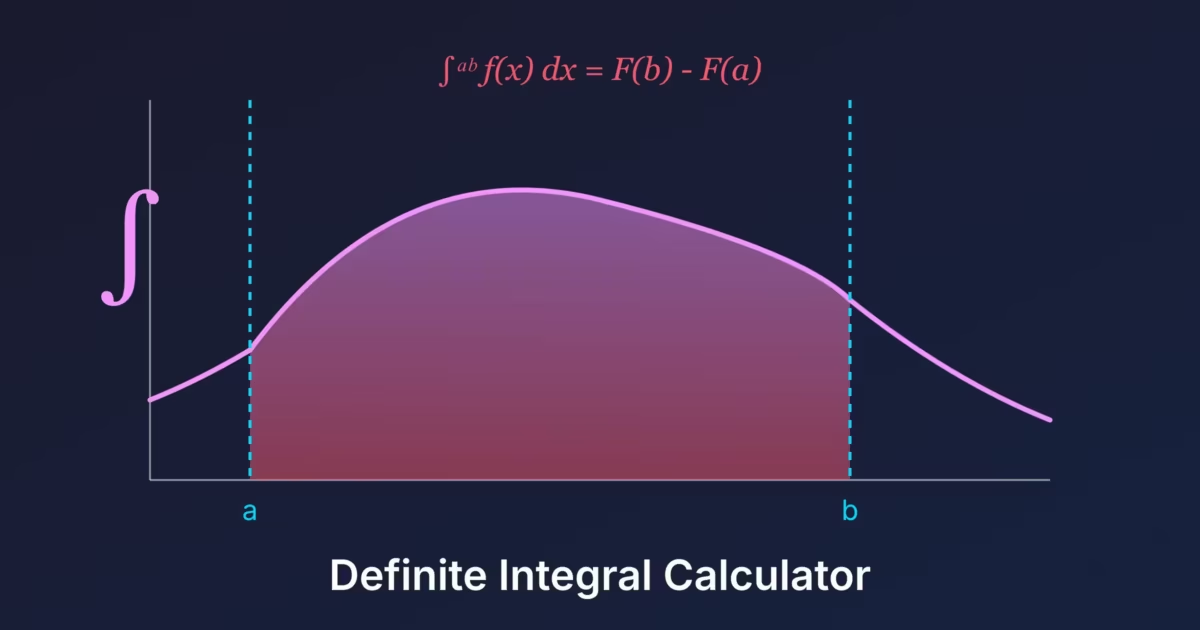
A definite integral calculates the net signed area between a function and the x-axis over a specific interval. Unlike indefinite integrals which give you a family of functions, definite integrals produce a single numerical value.
The notation \( \int_a^b f(x)\,dx \) represents the integral of \( f(x) \) from \( a \) to \( b \), where \( a \) is the lower limit and \( b \) is the upper limit of integration.
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
If \( F(x) \) is an antiderivative of \( f(x) \), then:
$$\int_a^b f(x)\,dx = F(b) – F(a)$$
This powerful theorem connects differentiation and integration, showing they’re inverse operations.
Signed Area
Above the x-axis
When \( f(x) > 0 \), the area contribution is positive. The region between the curve and the x-axis adds to the total.
Below the x-axis
When \( f(x) < 0 \), the area contribution is negative. This is why we call it “net signed area” rather than just area.
Properties of Definite Integrals
Additivity
$$\int_a^b f(x)\,dx + \int_b^c f(x)\,dx = \int_a^c f(x)\,dx$$
You can split integrals at any point.
Reversal
$$\int_a^b f(x)\,dx = -\int_b^a f(x)\,dx$$
Swapping limits changes the sign.
Linearity
$$\int_a^b [af(x) + bg(x)]\,dx = a\int_a^b f(x)\,dx + b\int_a^b g(x)\,dx$$
Constants factor out, and integrals distribute over addition.
Applications
Physics
- Work done by a force
- Displacement from velocity
- Charge from current
- Energy calculations
Geometry
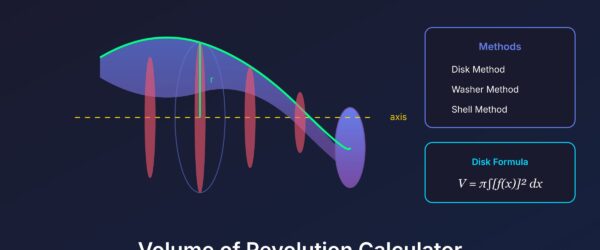
- Area between curves
- Volume of solids
- Arc length
- Surface area
Probability
- Expected values
- Cumulative distribution functions
- Probability density integration
Common Integrals
| Function | Integral |
|---|---|
| \( x^n \) | \( \frac{x^{n+1}}{n+1} \) |
| \( \frac{1}{x} \) | \( \ln |
| \( e^x \) | \( e^x \) |
| \( \sin(x) \) | \( -\cos(x) \) |
| \( \cos(x) \) | \( \sin(x) \) |
See more Integration Formulas.