Hypothesis Testing Calculator
Perform z-tests and t-tests for means and proportions with p-value calculation.
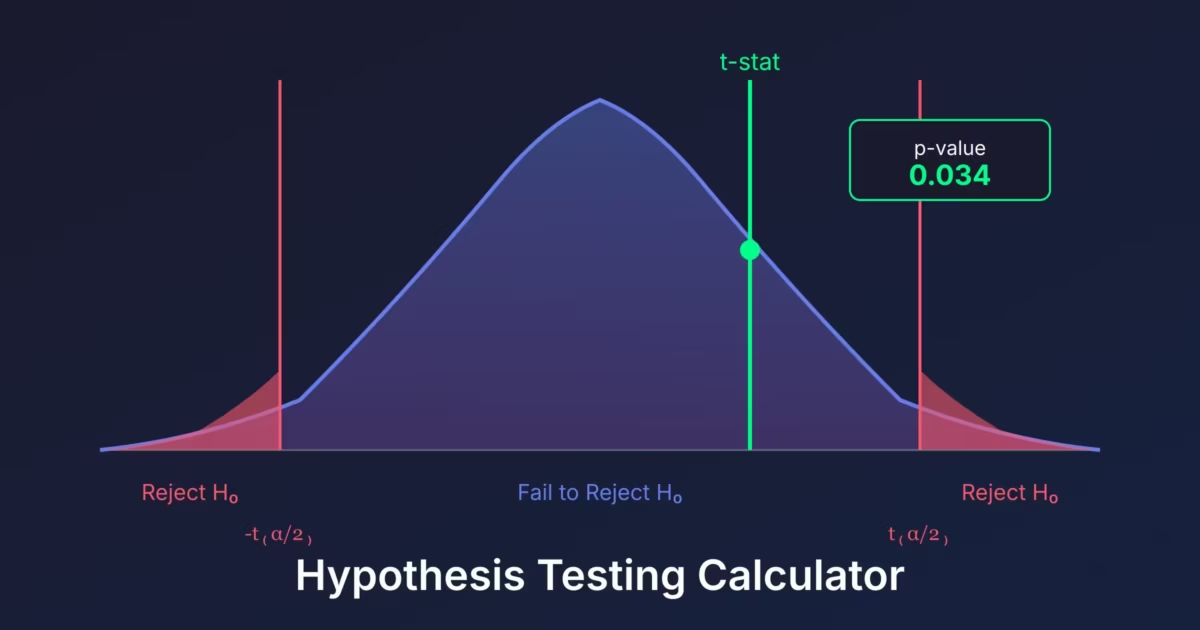
Test Result
Hypotheses
Test Statistics
Distribution
Interpretation
What is Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method for making decisions based on sample data. You start with a claim (hypothesis) about a population parameter and use data to determine whether there’s enough evidence to reject it.
The Hypotheses
Null Hypothesis (\( H_0 \))
The default assumption, typically stating “no effect” or “no difference.”
Example: \( H_0: \mu = 50 \) (the population mean equals 50)
Alternative Hypothesis (\( H_a \))
What you’re trying to find evidence for.
Example: \( H_a: \mu \neq 50 \) (the population mean differs from 50)
Test Types
Two-Tailed Test
Tests if the parameter differs from the hypothesized value in either direction.
$$H_a: \mu \neq \mu_0$$
Left-Tailed Test
Tests if the parameter is less than the hypothesized value.
$$H_a: \mu < \mu_0$$
Right-Tailed Test
Tests if the parameter is greater than the hypothesized value.
$$H_a: \mu > \mu_0$$
The P-Value
The p-value is the probability of observing results at least as extreme as the sample, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
- Small p-value → strong evidence against \( H_0 \)
- Large p-value → weak evidence against \( H_0 \)
Decision Rules
Using P-Value
- If p-value \( \leq \alpha \): Reject \( H_0 \)
- If p-value \( > \alpha \): Fail to reject \( H_0 \)
Using Critical Values
- If test statistic falls in rejection region: Reject \( H_0 \)
- Otherwise: Fail to reject \( H_0 \)
Significance Level (\( \alpha \))
The threshold for rejecting \( H_0 \), typically 0.05 (5%). This is the probability of making a Type I error (rejecting a true null hypothesis).
Types of Errors
Type I Error (\( \alpha \))
Rejecting \( H_0 \) when it’s actually true (false positive).
Type II Error (\( \beta \))
Failing to reject \( H_0 \) when it’s actually false (false negative).
Power = \( 1 – \beta \) (probability of correctly rejecting a false \( H_0 \))
Test Statistics
Z-Test (\( \sigma \) known)
$$z = \frac{\bar{x} – \mu_0}{\sigma / \sqrt{n}}$$
T-Test (\( \sigma \) unknown)
$$t = \frac{\bar{x} – \mu_0}{s / \sqrt{n}}$$
$$
Proportion Test
$$z = \frac{\hat{p} – p_0}{\sqrt{p_0(1-p_0)/n}}$$
Common Misconceptions
- P-value is NOT the probability \( H_0 \) is true
- Failing to reject \( H_0 \) doesn’t prove \( H_0 \) is true
- Statistical significance ≠ practical significance
Steps for Hypothesis Testing
- State the hypotheses (\( H_0 \) and \( H_a \))
- Choose significance level (\( \alpha \))
- Calculate the test statistic
- Find the p-value
- Make a decision
- State the conclusion in context