Key Challenges in Managing Sensitive Customer Data Online
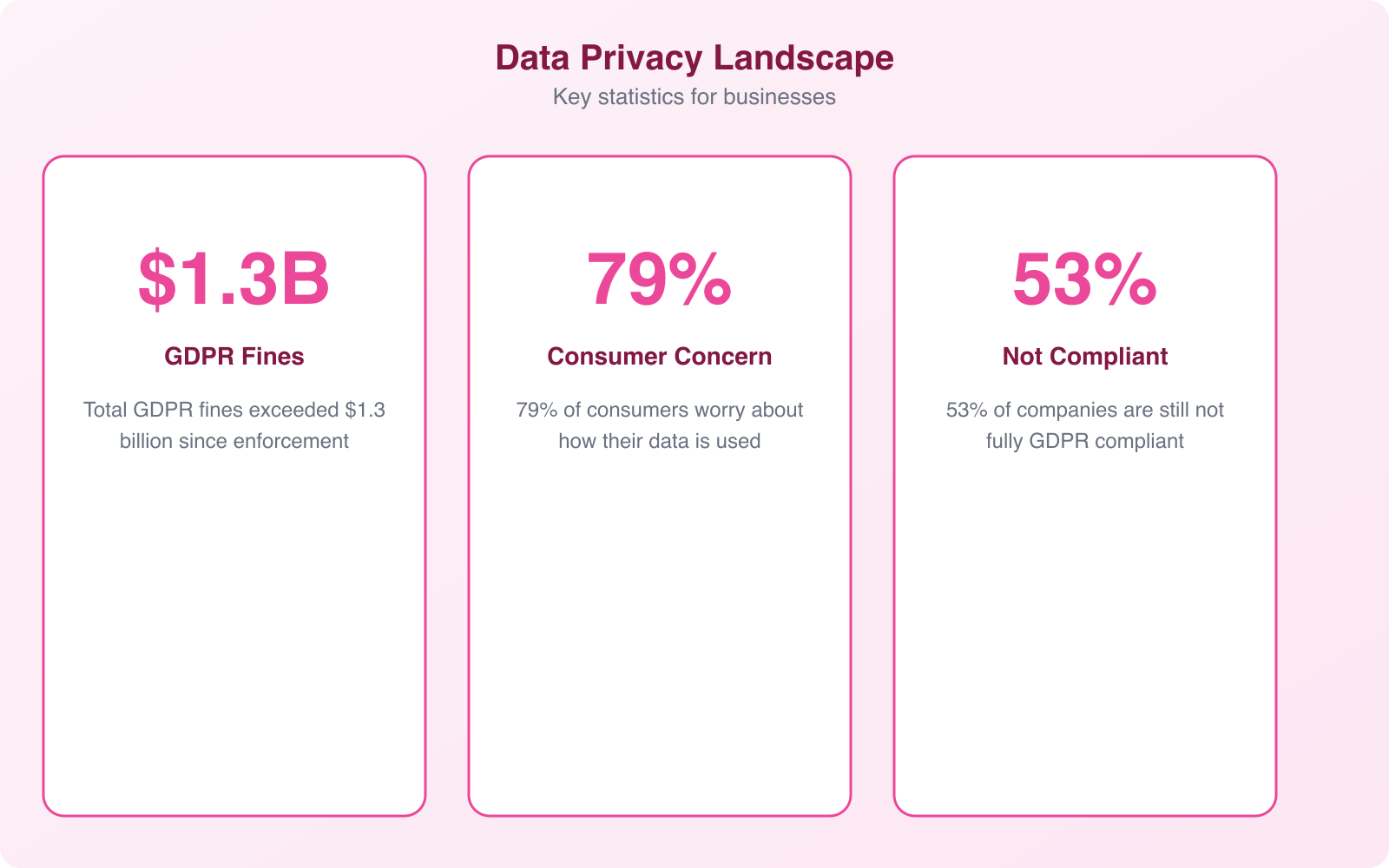
Every business that collects customer data makes a promise, whether they realize it or not. That promise is: “We’ll keep your information safe.” Breaking that promise doesn’t just trigger fines and lawsuits. It destroys the trust that took years to build. I’ve watched businesses lose 30-40% of their customer base after a single data breach, not because the breach was catastrophic, but because the response was slow and the protection was clearly inadequate.
Here are the biggest challenges businesses face when managing sensitive customer data online, and the practical strategies that actually work to address them.
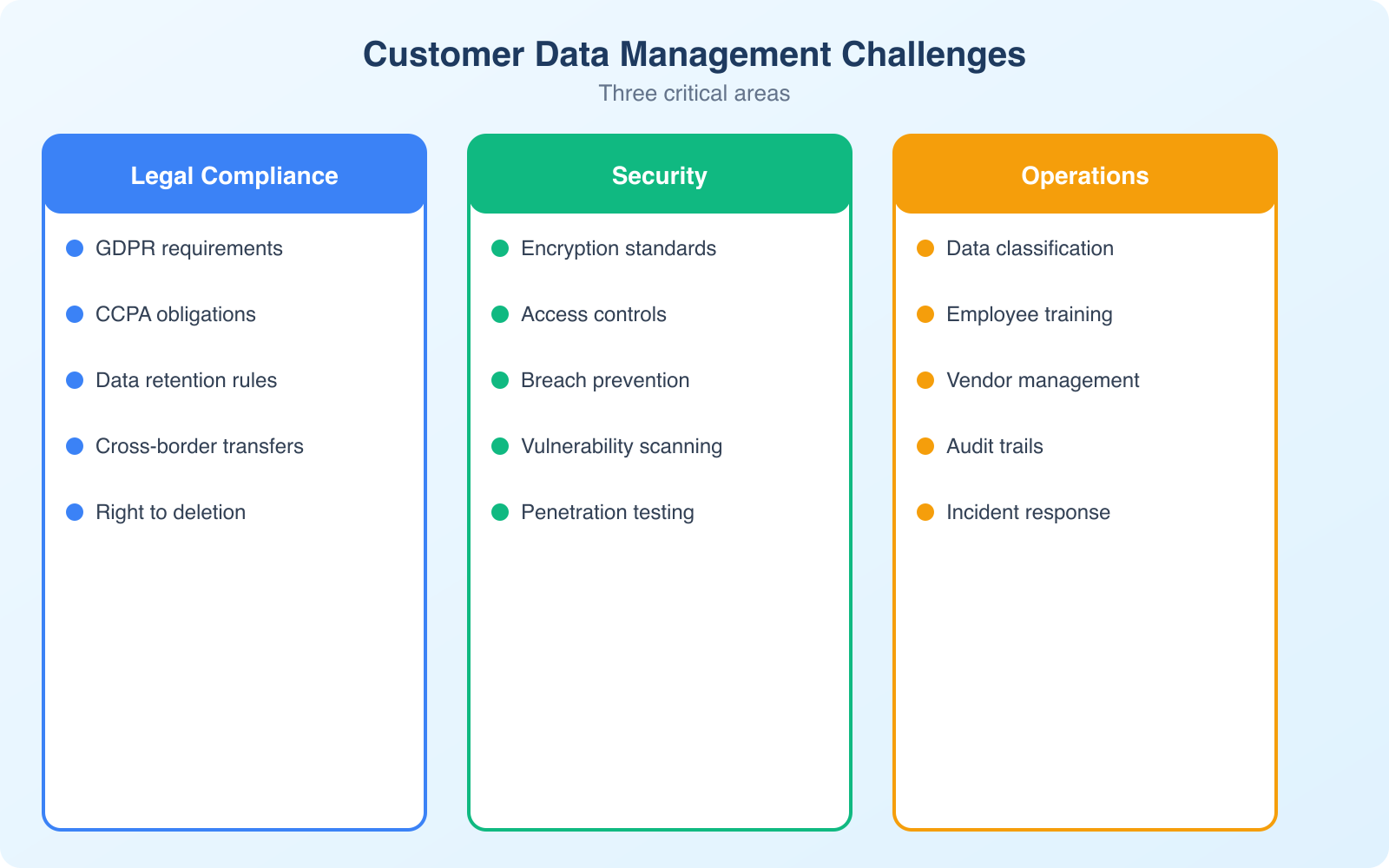
Navigating Constantly Changing Data Privacy Laws
The regulatory landscape for data privacy is a moving target. GDPR in Europe, CCPA/CPRA in California, PIPEDA in Canada, LGPD in Brazil, and new state-level laws passing in the US every year. If your business serves customers internationally, you’re potentially subject to dozens of overlapping regulations with different requirements.
The common thread across all these regulations: businesses must be transparent about what data they collect, get meaningful consent before collecting it, provide ways for customers to access or delete their data, and protect that data with reasonable security measures.
Practical steps to stay compliant:
- Implement a cookie consent management platform. Cookiebot handles consent banners, cookie scanning, and compliance documentation for GDPR and CCPA automatically.
- Maintain a data processing inventory. Document what data you collect, why, where it’s stored, who has access, and how long you keep it.
- Review your privacy policy quarterly. Laws change. Features change. Your privacy policy should reflect current reality, not what was true 2 years ago.
- Assign a data protection point person. Even if you can’t afford a full-time DPO, someone needs to be responsible for data compliance decisions.
Treating compliance as an ongoing process rather than a one-time checkbox is the only approach that works. The businesses that get fined are almost always the ones that set up a privacy policy in 2019 and never updated it.
Balancing Accessibility and Security
This is the tension every business faces: making data easily accessible to authorized users while keeping it locked down from everyone else. Customers expect seamless logins, instant account access, and personalized experiences. All of that requires handling sensitive data efficiently.
Personalization alone is worth up to $1 trillion in value according to McKinsey, but it relies on sensitive information to deliver. The challenge is enabling that personalization without creating security holes.
Common pitfalls and solutions:
- Single sign-on (SSO): Improves UX but creates a single point of failure. Mitigate by requiring MFA on the SSO provider account.
- API integrations: Connect your tools but can expose data if poorly configured. Use OAuth 2.0, rotate API keys regularly, and limit permissions to the minimum needed.
- Customer portals: Give users self-service access but must enforce session timeouts, strong authentication, and encrypted connections.
- Mobile access: Employees accessing company data on personal devices need device management policies and encryption requirements.
The key is layering security measures without destroying usability. Multi-factor authentication, encrypted connections, role-based access controls, and session management together create strong protection while keeping the user experience smooth.
Apply the principle of least privilege everywhere. Every employee, every API, every integration should have access to only the data it absolutely needs. When someone changes roles or leaves, revoke access the same day. Orphaned accounts with excessive permissions are one of the most common breach vectors.
Common Vulnerabilities Hackers Exploit
Hackers look for the path of least resistance. Most breaches don’t involve sophisticated zero-day exploits. They exploit basic mistakes that businesses make repeatedly:
- Weak or reused passwords: Credential stuffing attacks try leaked username/password pairs against multiple services. If your employees reuse passwords, one breach anywhere exposes everything.
- Outdated software: Unpatched systems have known vulnerabilities with publicly available exploit code. Keeping software updated is the simplest defense.
- Unsecured APIs: APIs that lack proper authentication or expose more data than necessary are prime targets. I’ve seen APIs that returned full customer records when only a name was needed.
- Misconfigured cloud storage: S3 buckets, Azure blobs, and Google Cloud Storage instances left publicly accessible. This happens more often than you’d think.
- Lack of encryption: Data intercepted during transfer is readable if not encrypted. TLS/SSL for websites and encrypted connections for APIs are mandatory.
Regular security audits catch these issues before attackers do. Schedule quarterly vulnerability scans and annual penetration tests. Use password management tools with MFA enforcement, and keep all software current.
Internal Policies That Make or Break Data Protection
Sometimes the biggest data risks come from inside the organization. Human error accounts for 95% of data breaches according to Infosecurity Magazine. Weak internal policies create opportunities for both accidental mistakes and intentional misuse.
Common internal failures:
- Employees with broader access than their role requires
- No monitoring or alerting for unusual data access patterns
- Personal devices used for work without encryption or device management
- No offboarding process that revokes system access when employees leave
- Lack of regular security awareness training
Build a culture of accountability. Limit access based on roles. Enforce strict BYOD (bring your own device) policies. Review access permissions quarterly. Train your team regularly on data handling procedures and phishing awareness.
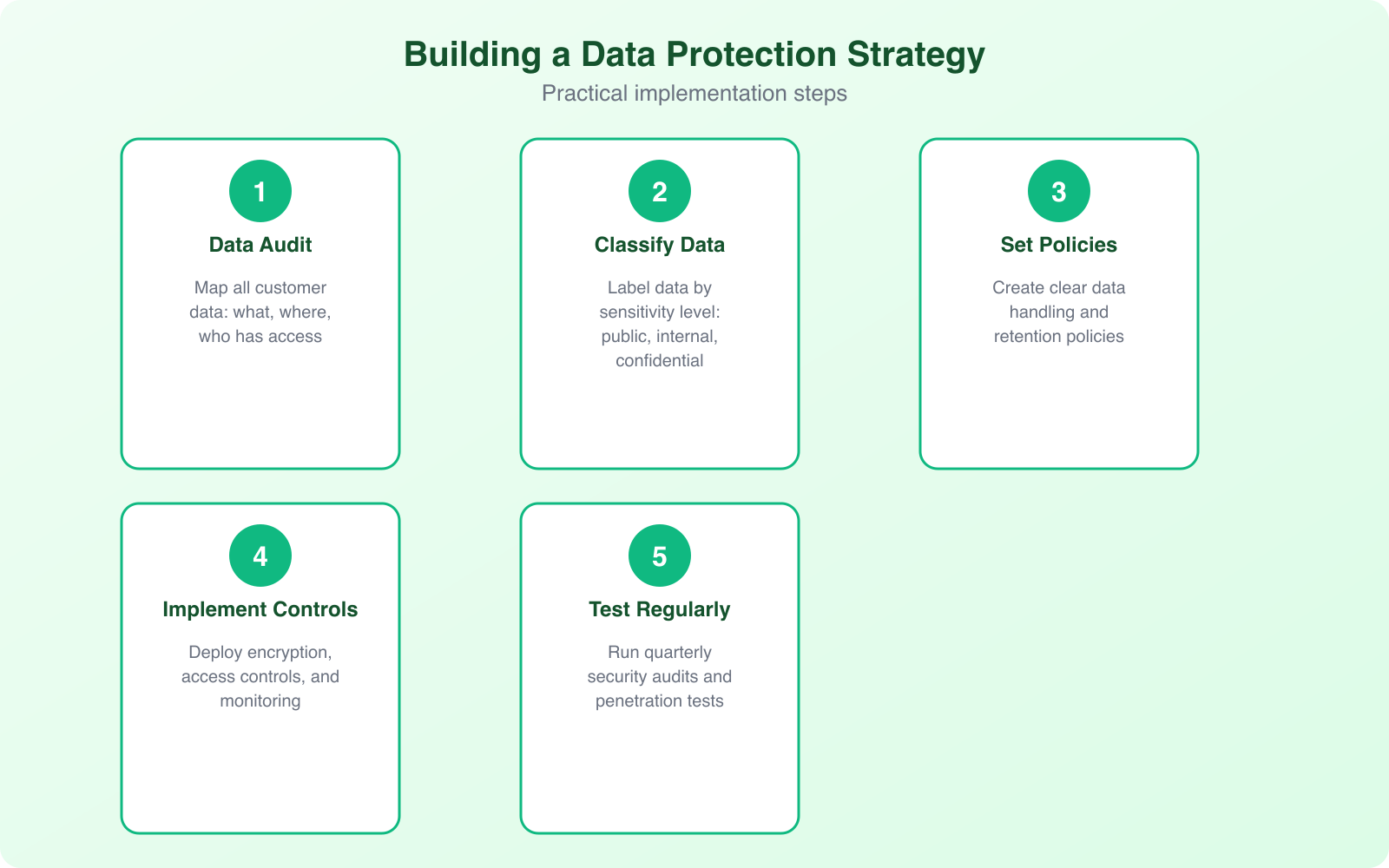
Building a Data Breach Response Plan
Every business that handles customer data needs a documented breach response plan. Not “we’ll figure it out when it happens.” An actual, written plan that everyone relevant has read and can execute under pressure.
Your plan should cover:
- Detection: How do you identify that a breach has occurred? What monitoring tools are in place?
- Containment: Immediate steps to stop the bleeding, including isolating affected systems.
- Assessment: Determining what data was affected, how many customers are impacted, and the severity.
- Notification: Who to tell (customers, regulators, law enforcement) and by when. GDPR requires 72-hour notification.
- Recovery: Restoring from backups, patching the vulnerability, and verifying that the threat is eliminated.
- Post-incident review: What went wrong, what worked, and how to prevent recurrence.
Test this plan annually with a tabletop exercise where your team walks through a simulated breach scenario. The first time you test your response plan should never be during an actual incident.
Keep a printed copy of your breach response plan accessible offline. If ransomware encrypts all your systems, you won’t be able to access a digital-only plan. A laminated checklist near the server room or IT office can save critical time.
Moving Forward: Making Data Protection a Business Priority
Managing sensitive customer data is a challenging, ongoing responsibility. The landscape keeps shifting as new regulations emerge, attack methods evolve, and customer expectations increase. But the businesses that treat data protection as a core competency rather than an afterthought consistently outperform those that don’t.
Practical steps like updating security policies, implementing encryption, training employees, and automating compliance significantly reduce risk. Combined with regular audits and a tested incident response plan, these measures create a defense that handles the vast majority of threats.
The investment in data protection isn’t just about avoiding fines. It’s about building the kind of trust that turns customers into long-term advocates. In a market where data breaches make headlines weekly, being the company that takes privacy seriously is a genuine competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What data privacy laws apply to my small business?
It depends on where your customers are located, not where your business is based. If you serve EU residents, GDPR applies. If you serve California residents, CCPA/CPRA applies. If you handle health data in the US, HIPAA may apply. Most businesses that operate online are subject to at least one data privacy regulation. Start with a cookie consent platform and a clear privacy policy.
How do I handle a customer’s data deletion request?
First, verify the requester’s identity. Then locate all instances of their data across your systems, including backups and third-party integrations. Delete or anonymize the data and confirm completion to the customer within the timeframe your applicable regulation requires (typically 30 days for GDPR, 45 days for CCPA). Document the process for compliance records.
What is the most common cause of customer data breaches?
Human error accounts for 95% of data breaches. The most common specific causes are phishing attacks that steal employee credentials, weak or reused passwords, misconfigured cloud storage, and unpatched software vulnerabilities. Technical sophistication from attackers is rarely needed when basic security hygiene is absent.
Do I need to encrypt all customer data?
At minimum, encrypt data in transit (using TLS/SSL for websites and APIs) and encrypt sensitive data at rest (payment information, personally identifiable information, health records). Full-disk encryption on employee devices is also recommended, especially for laptops that could be lost or stolen. Encryption is required by most privacy regulations.
How often should I audit my data security practices?
Run quarterly internal security reviews covering access permissions, software updates, and policy compliance. Conduct an annual comprehensive audit that includes vulnerability scanning and penetration testing. Additionally, review and update your privacy policy and data processing inventory whenever you add new tools, services, or data collection practices.
Disclaimer: This site is reader-supported. If you buy through some links, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. I only recommend tools I trust and would use myself. Your support helps keep gauravtiwari.org free and focused on real-world advice. Thanks. - Gaurav Tiwari